Mac Generate Ssh Key With Name
Generating SSH Keys for SFTP/SSH (FileZilla, Cyberduck, Dreamweaver, etc.) Two-factor authentication is becoming a security standard for large organizations. Many of you are already accustomed to using Duo to authenticate when using Box, WebEx or OSU Google GSuite apps. Chmod 400 idrsa. # Restrict read/write privileges to both keys; Instructions (Windows) Windows does not ship with software for generating SSH keys. Although many third party software packages can be used, this Lab Step uses PuTTYgen to generate SSH keys. Invoke PuTTYgen on your local Windows host. Leave the Parameters at their default values. To create a key pair using a third-party tool. Generate a key pair with a third-party tool of your choice. Save the public key to a local file. For example, /.ssh/my-key-pair.pub (Linux) or C: keys my-key-pair.pub (Windows). The file name extension for this file is not important. Creating a SSH Public Key on OSX¶. You generate an SSH key through Mac OS X by using the Terminal application. Once you upload a valid public SSH key, Gerrit can authenticate you based on this key. The terminal provides you with a text-based command line interface to the Unix shell of Mac OS X. Sep 15, 2014 If you are creating a key for the first time, click on the Generate Key button. You should then see a confirmation that the key was generated. Click on the Go Back button to return to the Manage SSH Keys page. You should see the Public key and the Private key generated with the name “idrsa”. 3) On Windows, generate your ssh key and transfer to MAC - for that Open Windows PowerShell and execute the follow commands: generate the key PSssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096.
Generate Ssh Key Windows
With a secure shell (SSH) key pair, you can create virtual machines (VMs) in Azure that use SSH keys for authentication, eliminating the need for passwords to sign in. This article shows you how to quickly generate and use an SSH public-private key file pair for Linux VMs. You can complete these steps with the Azure Cloud Shell, a macOS or Linux host, the Windows Subsystem for Linux, and other tools that support OpenSSH.
Note Ssh-keygen generate dsa key.
VMs created using SSH keys are by default configured with passwords disabled, which greatly increases the difficulty of brute-force guessing attacks.
For more background and examples, see Detailed steps to create SSH key pairs.
For additional ways to generate and use SSH keys on a Windows computer, see How to use SSH keys with Windows on Azure.
Supported SSH key formats
Azure currently supports SSH protocol 2 (SSH-2) RSA public-private key pairs with a minimum length of 2048 bits. Other key formats such as ED25519 and ECDSA are not supported.
Create an SSH key pair
Use the ssh-keygen command to generate SSH public and private key files. By default, these files are created in the ~/.ssh directory. You can specify a different location, and an optional password (passphrase) to access the private key file. If an SSH key pair with the same name exists in the given location, those files are overwritten.
The following command creates an SSH key pair using RSA encryption and a bit length of 4096:
If you use the Azure CLI to create your VM with the az vm create command, you can optionally generate SSH public and private key files using the --generate-ssh-keys option. The key files are stored in the ~/.ssh directory unless specified otherwise with the --ssh-dest-key-path option. The --generate-ssh-keys option will not overwrite existing key files, instead returning an error. In the following command, replace VMname and RGname with your own values:
Provide an SSH public key when deploying a VM
To create a Linux VM that uses SSH keys for authentication, specify your SSH public key when creating the VM using the Azure portal, Azure CLI, Azure Resource Manager templates, or other methods:
If you're not familiar with the format of an SSH public key, you can display your public key with the following cat command, replacing ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub with the path and filename of your own public key file if needed:
A typical public key value looks like this example:
If you copy and paste the contents of the public key file to use in the Azure portal or a Resource Manager template, make sure you don't copy any trailing whitespace. To copy a public key in macOS, you can pipe the public key file to pbcopy. Similarly in Linux, you can pipe the public key file to programs such as xclip.
The public key that you place on your Linux VM in Azure is by default stored in ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub, unless you specified a different location when you created the key pair. To use the Azure CLI 2.0 to create your VM with an existing public key, specify the value and optionally the location of this public key using the az vm create command with the --ssh-key-values option. In the following command, replace VMname, RGname, and keyFile with your own values:
If you want to use multiple SSH keys with your VM, you can enter them in a space-separated list, like this --ssh-key-values sshkey-desktop.pub sshkey-laptop.pub.
SSH into your VM
With the public key deployed on your Azure VM, and the private key on your local system, SSH into your VM using the IP address or DNS name of your VM. In the following command, replace azureuser and myvm.westus.cloudapp.azure.com with the administrator user name and the fully qualified domain name (or IP address):
If you specified a passphrase when you created your key pair, enter that passphrase when prompted during the login process. The VM is added to your ~/.ssh/known_hosts file, and you won't be asked to connect again until either the public key on your Azure VM changes or the server name is removed from ~/.ssh/known_hosts.
If the VM is using the just-in-time access policy, you need to request access before you can connect to the VM. For more information about the just-in-time policy, see Manage virtual machine access using the just in time policy.
Next steps
For more information on working with SSH key pairs, see Detailed steps to create and manage SSH key pairs.
If you have difficulties with SSH connections to Azure VMs, see Troubleshoot SSH connections to an Azure Linux VM.
Updated by LinodeWritten by Linode
Report an Issue View File Edit File
Password authentication is the default method most SSH (Secure Shell) clients use to authenticate with remote servers, but it suffers from potential security vulnerabilities, like brute-force login attempts. An alternative to password authentication is public key authentication, in which you generate and store on your computer a pair of cryptographic keys and then configure your server to recognize and accept your keys. Using key-based authentication offers a range of benefits:
Key-based login is not a major target for brute-force hacking attacks.
If a server that uses SSH keys is compromised by a hacker, no authorization credentials are at risk of being exposed.
Because a password isn’t required at login, you are able to able to log in to servers from within scripts or automation tools that you need to run unattended. For example, you can set up periodic updates for your servers with a configuration management tool like Ansible, and you can run those updates without having to be physically present.
This guide will explain how the SSH key login scheme works, how to generate an SSH key, and how to use those keys with your Linode.
NoteHow SSH Keys Work
SSH keys are generated in pairs and stored in plain-text files. The key pair (or keypair) consists of two parts:
A private key, usually named
id_rsa. The private key is stored on your local computer and should be kept secure, with permissions set so that no other users on your computer can read the file.Caution
A public key, usually named
id_rsa.pub. The public key is placed on the server you intend to log in to. You can freely share your public key with others. If someone else adds your public key to their server, you will be able to log in to that server.
When a site or service asks for your SSH key, they are referring to your SSH public key (id_rsa.pub). For instance, services like GitHub and Gitlab allow you to place your SSH public key on their servers to streamline the process of pushing code changes to remote repositories.
The authorized_keys File
In order for your Linode to recognize and accept your key pair, you will need to upload your public key to your server. More specifically, you will need to upload your public key to the home directory of the user you would like to log in as. If you would like to log in to more than one user on the server using your key pair, you will need to add your public key to each of those users.
To set up SSH key authentication for one of your server’s users, add your public key to a new line inside the user’s authorized_keys file. This file is stored inside a directory named .ssh/ under the user’s home folder. A user’s authorized_keys file can store more than one public key, and each public key is listed on its own line. If your file contains more than one public key, then the owner of each key listed will be able to log in as that user.
Granting Someone Else Access to your Server
To give someone else access to your server’s user, simply add their public key on a new line in your authorized_keys file, just as you would add your own. To revoke access for that person, remove that same line and save the changes.
Challenge-Response
When logging in to a server using SSH, if there is a public key on file on that server, the server will create a challenge. This challenge will be crafted in such a way that only the holder of the private SSH key will be able to decipher it.
This challenge-response action happens without any user interaction. If the person attempting to log in has the corresponding private key, then they will be safely logged in. If not, the login will either fail or fall back to a password-based authentication scheme.
SSH Key Passphrases
You can optionally provide an additional level of security for your SSH keys by encrypting them with a passphrase at the time of creation. When you attempt to log in using an encrypted SSH key, you will be prompted to enter its passphrase. This is not to be confused with a password, as this passphrase only decrypts the key file locally and is not transferred over the Internet as a password might be.
If you’d like to set up your logins so that they require no user input, then creating a passphrase might not be desirable, but it is strongly recommended nevertheless.
Linux and macOS
Generate a Key Pair
Perform the steps in this section on your local machine.
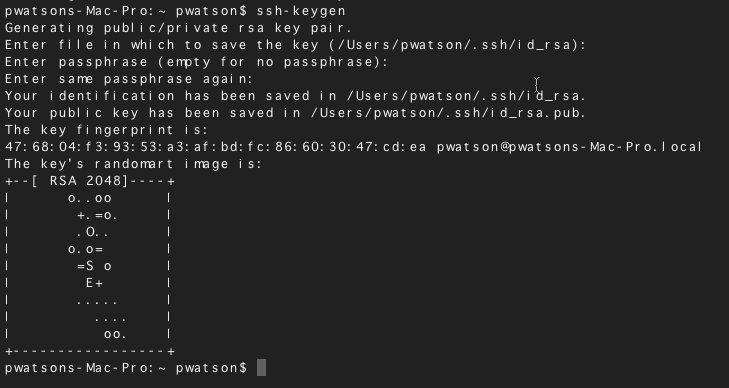
Create a new key pair.
Caution
This command will overwrite an existing RSA key pair, potentially locking you out of other systems.
If you’ve already created a key pair, skip this step. To check for existing keys, run
ls ~/.ssh/id_rsa*.If you accidentally lock yourself out of the SSH service on your Linode, you can still use the Lish console to login to your server. After you’ve logged in via Lish, update your
authorized_keysfile to use your new public key. This should re-establish normal SSH access.The
-bflag instructsssh-keygento increase the number of bits used to generate the key pair, and is suggested for additional security.Press Enter to use the default names
id_rsaandid_rsa.pubin the/home/your_username/.sshdirectory before entering your passphrase.While creating the key pair, you will be given the option to encrypt the private key with a passphrase. This means that the key pair cannot be used without entering the passphrase (unless you save that passphrase to your local machine’s keychain manager). We suggest that you use the key pair with a passphrase, but you can leave this field blank if you don’t want to use one.
Upload your Public Key
There are a few different ways to upload your public key to your Linode from Linux and macOS client systems:
Using ssh-copy-id
ssh-copy-id is a utility available on some operating systems that can copy a SSH public key to a remote server over SSH.
To use
ssh-copy-id, pass your username and the IP address of the server you would like to access:You’ll see output like the following, and a prompt to enter your user’s password:
Verify that you can log in to the server with your key.
Using Secure Copy (scp)
Secure Copy (scp) is a tool that copies files from a local computer to a remote server over SSH:
authorized_keys file on your server. If you have already set up other public keys on your server, use the ssh-copy-id command or enter your key manually.Connect to your server via SSH with the user you would like to add your key to:
Create the
~/.sshdirectory andauthorized_keysfile if they don’t already exist:Give the
~/.sshdirectory andauthorized_keysfiles appropriate file permissions:In another terminal on your local machine, use
scpto copy the contents of your SSH public key (id_rsa.pub) into theauthorized_keysfile on your server. Substitute in your own username and your server’s IP address:Verify that you can log in to the server with your key.
Manually Copy an SSH Key
Generate Ssh Key Github
You can also manually add an SSH key to a server:
Begin by copying the contents of your public SSH key on your local computer. You can use the following command to output the contents of the file:
You should see output similar to the following:
Note that the public key begins with
ssh-rsaand ends with[email protected].Once you have copied that text, connect to your server via SSH with the user you would like to add your key to:
Create the
~/.sshdirectory andauthorized_keysfile if they don’t already exist:Give the
~/.sshdirectory andauthorized_keysfiles appropriate file permissions:Open the
authorized_keysfile with the text editor of your choice (nano, for example). Then, paste the contents of your public key that you copied in step one on a new line at the end of the file.Save and close the file.
Note
If you initially logged into the server as
rootbut edited theauthorized_keysfile of another user, then the.ssh/folder andauthorized_keysfile of that user may be owned byroot. Set that other user as the files’ owner:Verify that you can log in to the server with your key.
Connect to the Remote Server
SSH into the server from your local machine:
If you chose to use a passphrase when creating your SSH key, you will be prompted to enter it when you attempt to log in. Depending on your desktop environment, a window may appear:
Caution
Do not allow the local machine to remember the passphrase in its keychain unless you are on a private computer which you trust.You may also see the passphrase prompt at your command line:
Enter your password. You should see the connection establish in the local terminal.
Windows
The following instructions use the PuTTY software to connect over SSH, but other options are available on Windows too.
Generate a Key Pair with PuTTY
Download PuTTYgen (
puttygen.exe) and PuTTY (putty.exe) from the official site.Launch
puttygen.exe. TheRSAkey type at the bottom of the window is selected by default for an RSA key pair butED25519(EdDSA using Curve25519) is a comparable option if your remote machine’s SSH server supports DSA signatures. Do not use theSSH-1(RSA)key type unless you know what you’re doing.Increase the RSA key size from
2048bits4096and click Generate:PuTTY uses the random input from your mouse to generate a unique key. Once key generation begins, keep moving your mouse until the progress bar is filled:
When finished, PuTTY will display the new public key. Right-click on it and select Select All, then copy the public key into a Notepad file.
Save the public key as a
.txtfile or some other plaintext format. This is important–a rich text format such as.rtfor.doccan add extra formatting characters and then your private key won’t work:Enter a passphrase for the private key in the Key passphrase and Confirm passphrase text fields. Important: Make a note of your passphrase, you’ll need it later:
Click Save private key. Choose a file name and location in Explorer while keeping the
ppkfile extension. If you plan to create multiple key pairs for different servers, be sure to give them different names so that you don’t overwrite old keys with new:
Manually Copy the SSH Key with PuTTY
Launch
putty.exe. Find the Connection tree in the Category window, expand SSH and select Auth. Click Browse and navigate to the private key you created above:Scroll back to the top of the Category window and click Session. Enter the hostname or IP address of your Linode. PuTTY’s default TCP port is
22, the IANA assigned port for for SSH traffic. Change it if your server is listening on a different port. Name the session in the Saved Sessions text bar and click Save:Click the Open button to establish a connection. You will be prompted to enter a login name and password for the remote server.
Once you’re logged in to the remote server, configure it to authenticate with your SSH key pair instead of a user’s password. Create an
.sshdirectory in your home directory on your Linode, create a blankauthorized_keysfile inside, and set their access permissions:Open the
authorized_keysfile with the text editor of your choice (nano, for example). Then, paste the contents of your public key that you copied in step one on a new line at the end of the file.Save, close the file, and exit PuTTY.
Verify that you can log in to the server with your key.
Using WinSCP
Uploading a public key from Windows can also be done using WinSCP:
Cautionauthorized_keys file on your server. If you have already set up other public keys on your server, use the PuTTY instructions instead.In the login window, enter your Linode’s public IP address as the hostname, the user you would like to add your key to, and your user’s password. Click Login to connect.
Once connected, WinSCP will show two file tree sections. The left shows files on your local computer and the right shows files on your Linode. Using the file explorer on the left, navigate to the file where you saved your public key in Windows. Select the public key file and click Upload in the toolbar above.
You’ll be prompted to enter a path on your Linode where you want to upload the file. Upload the file to
/home/your_username/.ssh/authorized_keys.Verify that you can log in to the server with your key.
Connect to the Remote Server with PuTTY
Start PuTTY and Load your saved session. You’ll be prompted to enter your server user’s login name as before. However, this time you will be prompted for your private SSH key’s passphrase rather than the password for your server’s user. Enter the passphrase and press Enter.
Troubleshooting
If your SSH connections are not working as expected, or if you have locked yourself out of your system, review the Troubleshooting SSH guide for troubleshooting help.
Upload your SSH Key to the Cloud Manager
It is possible to provision each new Linode you create with an SSH public key automatically through the Cloud Manager.
Log in to the Cloud Manager.
Click on your username at the top right hand side of the page. Then click on My Profile in the dropdown menu that appears:
Note
If you are viewing the Cloud Manager in a smaller browser window or on a smaller device, then the My Profile link will appear in the sidebar links. To view the sidebar links, click on the disclosure button to the left of the blue Create button at the top of the page.From the My Profile page, select the SSH Keys tab, and then click Add a SSH Key:
Create a label for your key, then paste in the contents of your public SSH key (
id_rsa.pub):Click Add Key.
When you next create a Linode you’ll be given the opportunity to include your SSH key in the Linode’s creation. This key will be added to the root user of the new Linode.
In the Create Linode form, select the SSH key you’d like to include. This field will appear below the Root Password field:
Next Steps
After you set up your SSH keys and confirm they are working as expected, review the How to Secure Your Server guide for instructions on disabling password authentication for your server.
Join our Community
This guide is published under a CC BY-ND 4.0 license.